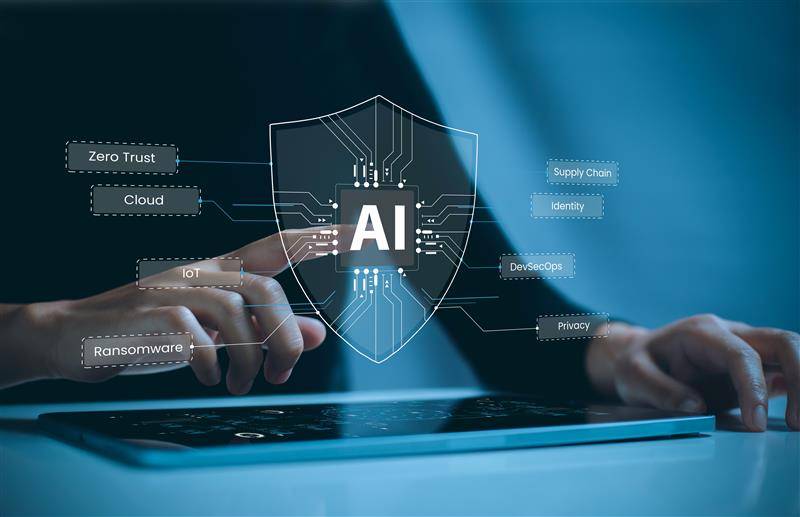
Cybersecurity today has turned into a modern battlefield; attackers and defenders constantly struggle with each other. Armed with AI tech, cyber attackers now have tools that make their threats powerful and hard to stop. This technology is also changing how cyber threats work, making it essential for organisations to use AI to defend themselves.
AI-Driven Cyber Threats: Cyber attackers have powerful AI tools, allowing them to carry out complex and dangerous attacks. Here are ways in which AI is worsening threats:
- Automated Attacks: AI can help attackers plan and carry out fast and organised attacks. This allows them to quickly launch large-scale attacks.
- Adaptable Tactics: AI can help attackers change their tactics in real-time. This makes it difficult for defenders to keep up with the constantly evolving methods of attack.
- Smart Scams: AI can help attackers create convincing scams, like phishing emails, that trick people into revealing sensitive information.
- Advanced Malware: AI helps attackers create malware that can avoid being detected by traditional security systems.
- Targeted Attacks: AI can identify specific targets within an organisation, like important people or valuable information, to make attacks effective.
Because of AI, a single attacker can use automated tools to launch complex, large-scale attacks that were once only possible for bigger, well-resourced adversaries.
AI for Defenders: While AI makes attacks dangerous, it can also help defenders protect their systems. Here’s how defenders can use AI to stay ahead:
- Faster Threat Detection: AI can scan large amounts of data quickly to find signs of cyberattacks, allowing defenders to respond faster.
- Automated Responses: AI can help defenders automatically block harmful actions, isolate affected systems, and fix problems without human intervention.
- Predicting Future Threats: AI can analyse patterns from past attacks to predict what threats might happen next, allowing defenders to prepare in advance.
- Better Intelligence: AI can help defenders gather and analyse information about threats from different sources, improving their ability to respond to attacks.
- Behaviour Monitoring: AI can watch how users and systems behave to spot unusual activities that might signal a cyberattack, helping catch threats early.
By using AI, defenders can improve their response time, predict attacks, and protect their systems more effectively.
Cybersecurity Roles
With the advent of generative AI and blockchain technology, the need for cybersecurity engineers and analysts has increased. Demand is particularly high in the following fields:
System and Network Management
Effective management of systems and networking is essential for any cybersecurity professional. A thorough understanding of network design, policies, and system architecture is necessary to identify vulnerabilities and implement strong protections. Apart from configuring firewalls and safeguarding network data, security experts must stay current with emerging technologies like Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
Programming Languages
Proficiency in programming languages is highly valuable. By mastering C, PHP, HTML, Java, Python, and SQL, experts can create custom programs for routine security tasks, develop secure applications, and identify vulnerabilities in existing software. SQL expertise is crucial for database security, given the rise in data theft and hacking attacks targeting systems.
Cloud Security
With the growing use of cloud computing, cybersecurity professionals must understand cloud architecture and its interaction with various devices and networks. Cloud security, including securing data storage and cloud environments, is an expanding field. Knowledge of cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform is essential for those working in cybersecurity.
Blockchain Technology
Though primarily associated with digital currency, blockchain is also a powerful security tool due to its decentralised nature and resistance to tampering. By distributing data across multiple devices, blockchain creates a network highly resistant to hacking or data deletion. Cybersecurity professionals who understand the risks and benefits of blockchain technology will be in high demand, especially as industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management adopt blockchain solutions.
Communication Skills
Strong communication skills are crucial. Professionals must be able to explain complex security concepts clearly, whether collaborating with other departments to build secure systems, educating staff on security protocols, or presenting risks to senior management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is transforming cybersecurity by enhancing threat detection and analysis. AI algorithms can process large volumes of data quickly, identifying patterns related to vulnerabilities and attacks. Additionally, AI-powered solutions can manage routine tasks like threat detection, analysis, and response, allowing cybersecurity teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Conclusion
AI is changing the landscape of cyber threats. Attackers are using it to create smarter, faster, and targeted attacks, making it harder for organisations to defend themselves. However, defenders can also use AI to improve their security, stay ahead of attacks, and respond quickly. In today’s digital world, using AI in cybersecurity is essential to protect against the evolving threat landscape. Organisations must invest in AI tools to stay safe from increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.